研究背景:工业革命后,大气中温室气体含量升高,地球陆地圈与大气圈能量收支平衡与物质循环过程发生改变,全球温度不断升高,并由此带来一系列极端气候事件。IPCC第六次评估报告指出,1970-2020年是最近2000年中最热的50年,与1850-1990年相比,2011-2020年的全球平均气温升高1.09 ℃。中国是全球气候变化的敏感区和影响显著区,1951-2020年我国升温速率高达0.26℃/10a,远高于全球平均水平(0.15℃/10a),21世纪末平均气温或将上升4°C。气候变暖会导致大气边界层容纳水汽能力增强,大气水汽含量上升,造成极端降雨强度增加。极端降雨是极端气候的典型表现,具有突发性、破坏性、区域性,易诱发地质灾害,给社会、经济和人民生活造成严重影响。因此,明晰气候变化背景下,极端降雨变化特征及其对气温变化的响应,对区域可持续发展至关重要。
中国贵州省受来自太平洋的东南季风与印度洋的西南季风影响,降雨丰沛。但其下垫面结构复杂,降雨空间分布不均,易形成极端降雨,增加地质灾害发生的风险。研究以贵州省为例,从区域角度出发,分析不同下垫面条件下,历史、未来两个时期贵州省极端降雨特征及其对气温变化的响应,为气温变化背景下区域防灾减灾提供决策依据。
研究成果:Characterization of extreme rainfall changes and response to temperature changes in Guizhou Province, China
成果作者:谭红梅,贺中华*,余欢,等
成果简介:不同时期、不同下垫面条件下极端降雨表现出不同特征,其对气候变化的响应也不同。贵州地形地貌复杂,降雨空间分布不均,易形成极端降雨,增加地质灾害发生的风险。针对贵州省极端气候的研究,大多关注其时空特征与模式数据预估,缺乏探究其在不同下垫面条件下,极端降雨变化特征及其对气温变化的响应研究。本文基于贵州省31个站点1990-2020、2021-2100年两个时期逐日降雨数据计算极端降雨,分析贵州省极端降雨时间、空间以及重现期特征,探讨极端降雨对气温变化的响应关系。结果表明:(1)贵州历史、未来两个时期极端降雨时间上均呈上升趋势,空间上分别呈“南高北低、东高西低”、“东南高、西北低”的分布格局;两时期极端降雨估计量均随重现期增加而增大,且各重现期下极端降雨空间分布都与非重现期一致;(2)贵州历史、未来两个时期气温均表现升高趋势,且两时期气温空间分布格局与极端降雨分布相似;(3)不同时期、不同下垫面条件下,极端降雨强度随气温升高的变化几乎都大于C-C率;极端降雨对气温变化均呈Hook响应结构,且气候响应结构会随气候变暖右移。研究结果可为气温变化背景下区域防灾减灾提供决策依据。
成果图表:
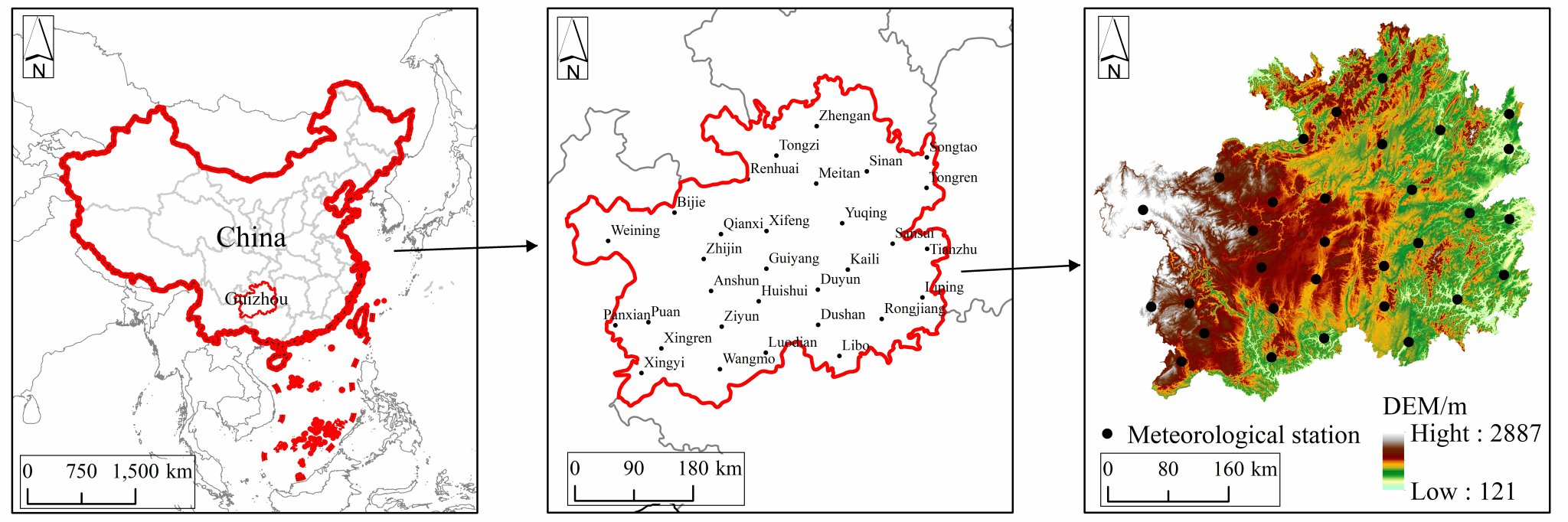
Fig. 1 Geomorphology of the study area and meteorological stations distribution.

Fig. 2 Graph of structural grading results of the subsurface.
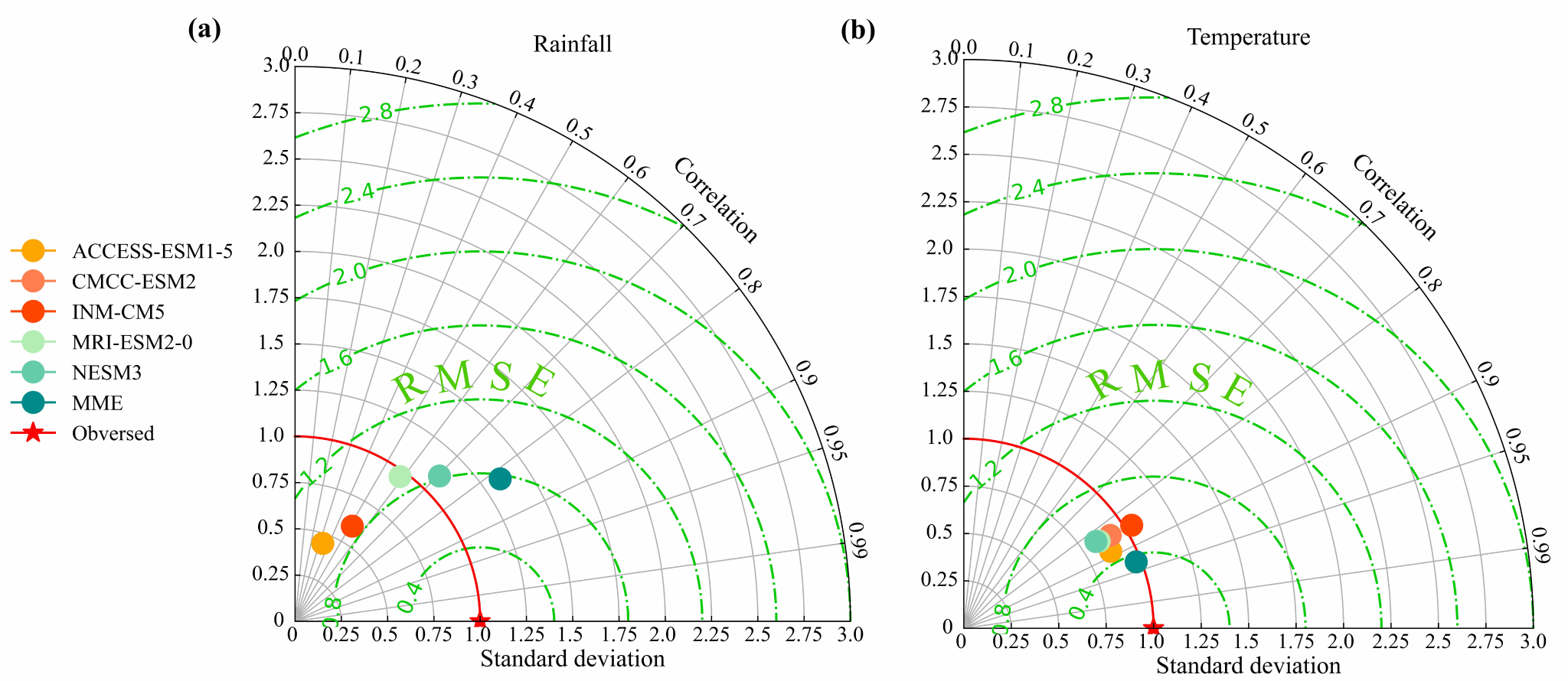
Fig. 3 Taylor diagram of CMIP6 model data for simulation of rainfall and temperature in Guizhou.
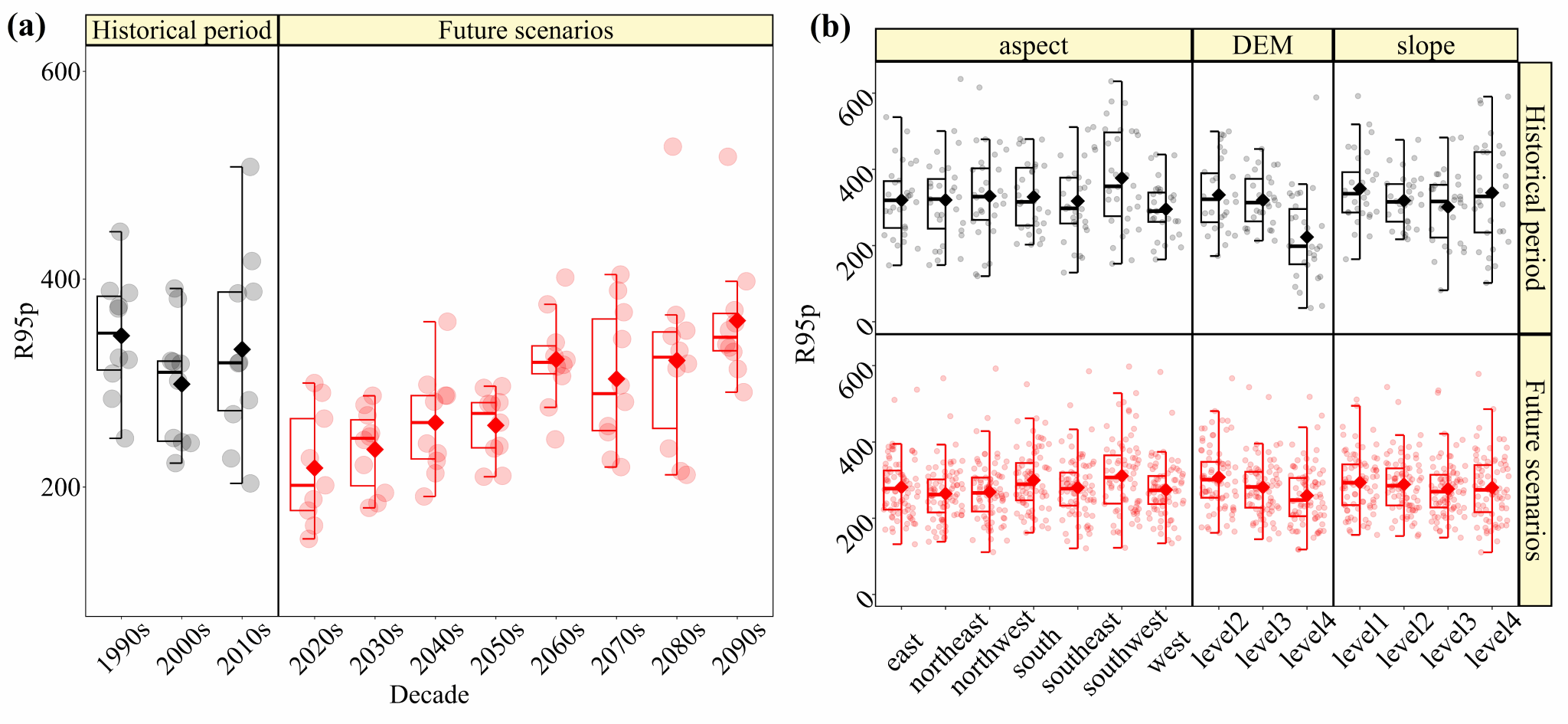
Fig. 4 Boxplots of R95p as a whole and under different subsurface conditions.
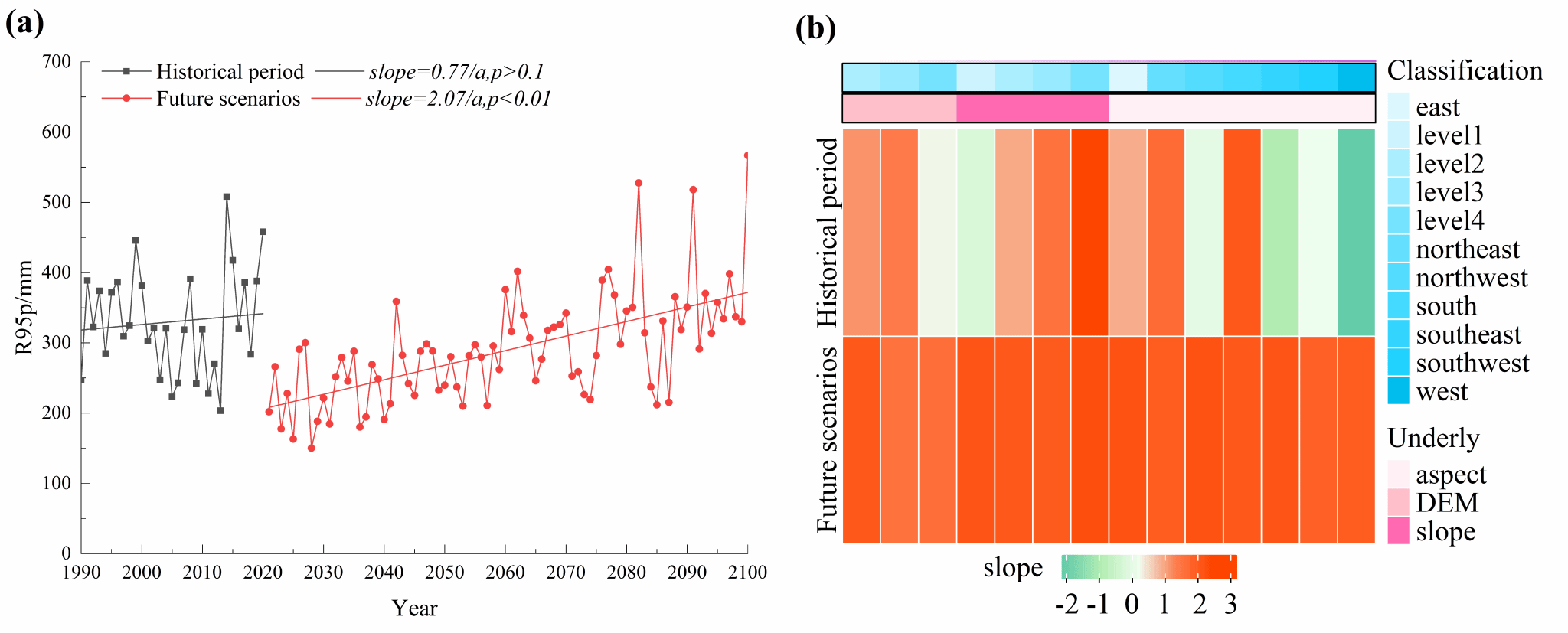
Fig. 5 Trends of R95p as a whole and under different subsurface conditions.
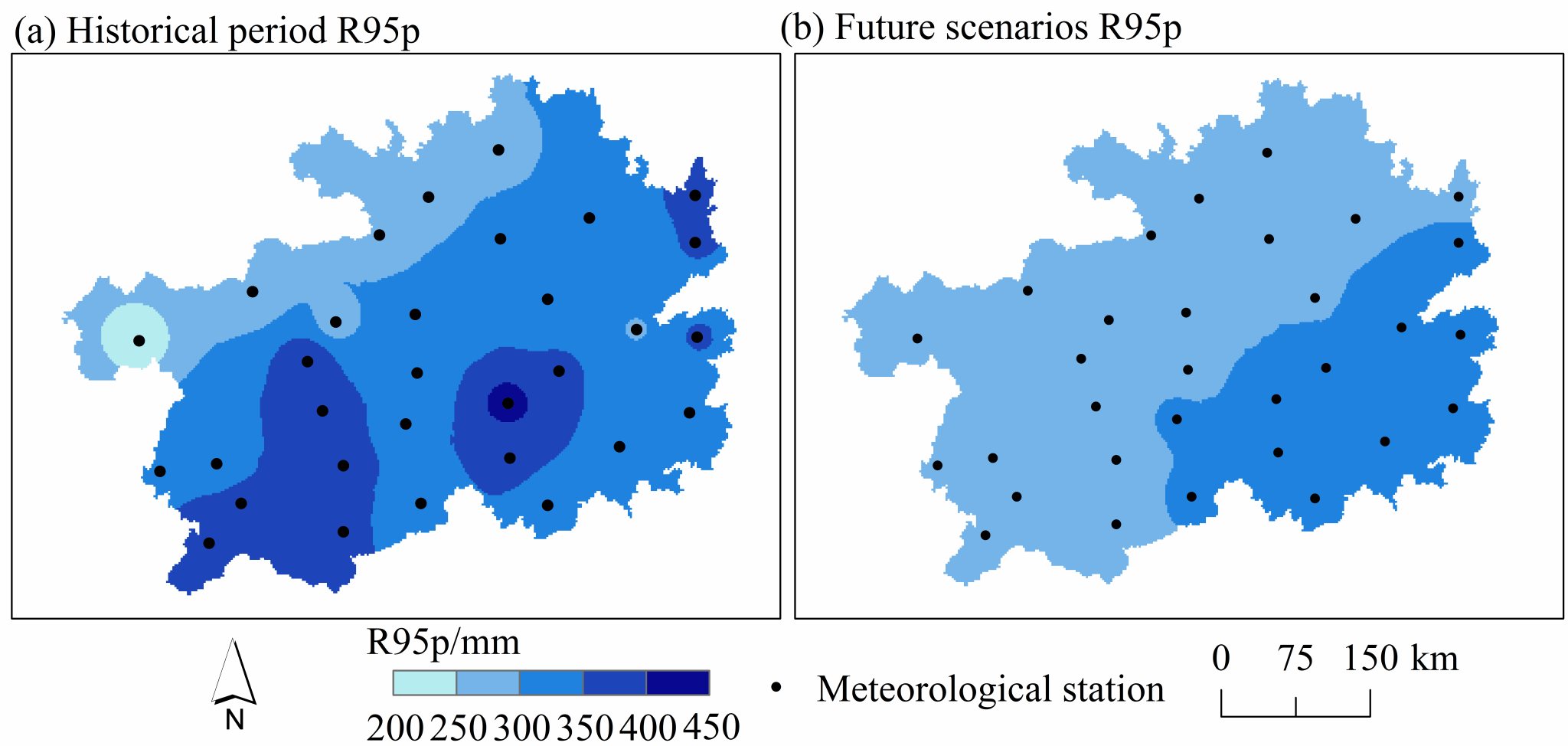
Fig. 6 Spatial distribution of R95p in historical and future periods.
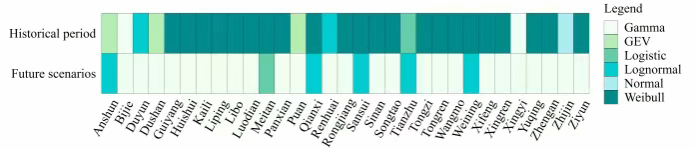
Fig. 7 Plot of the optimal site distribution function.
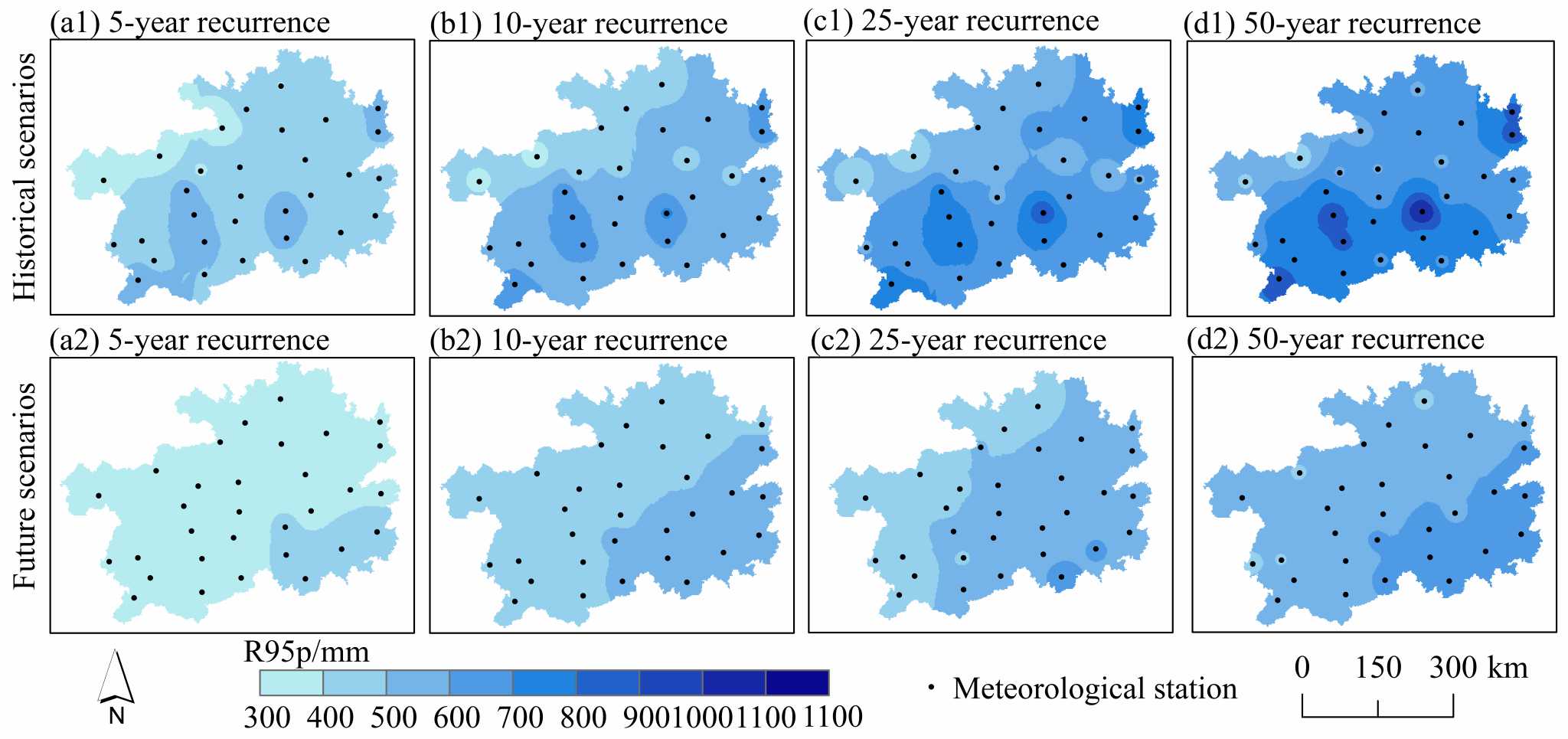
Fig. 8 R95p recurrence spatial distribution.
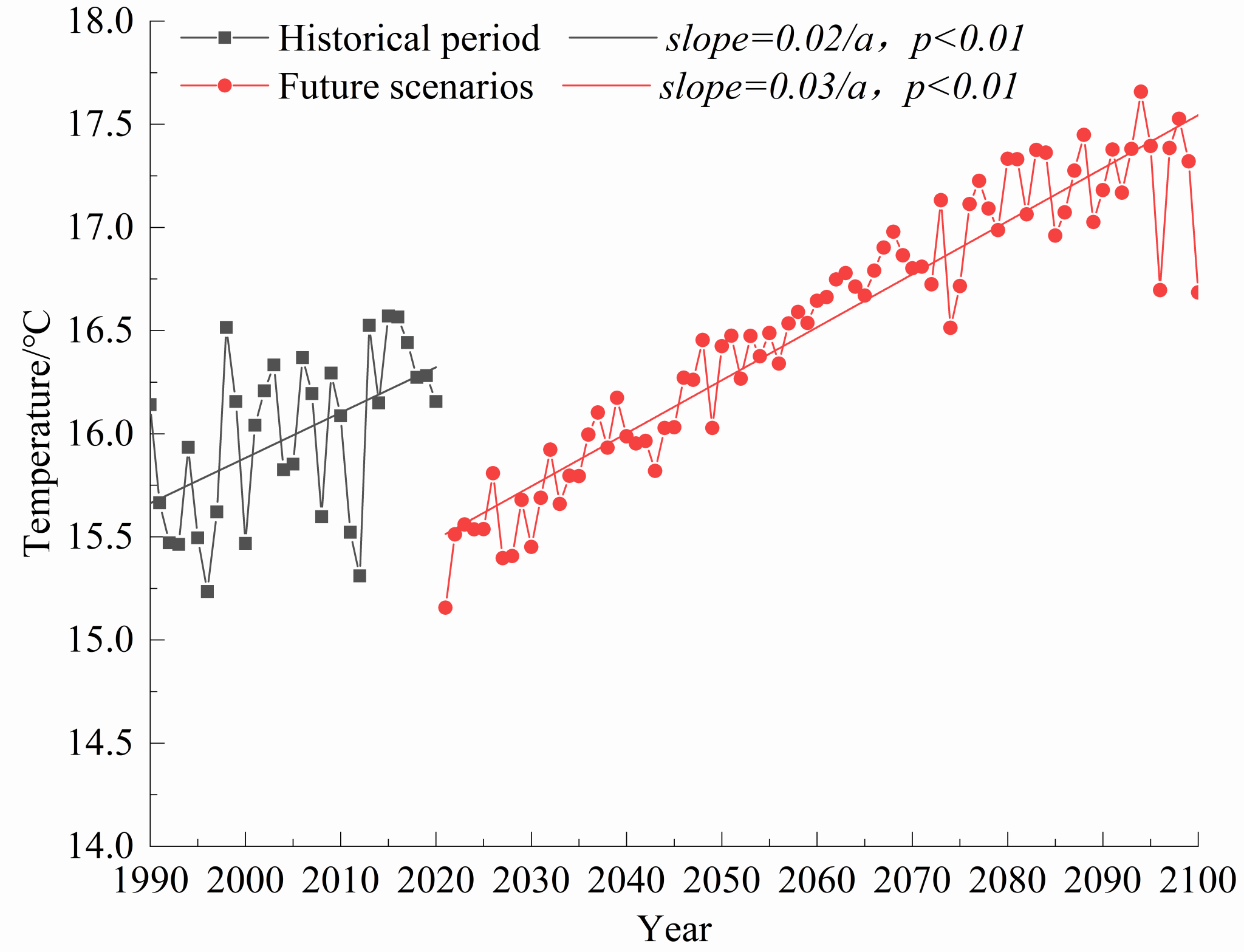
Fig.9 Temperature time change trend.
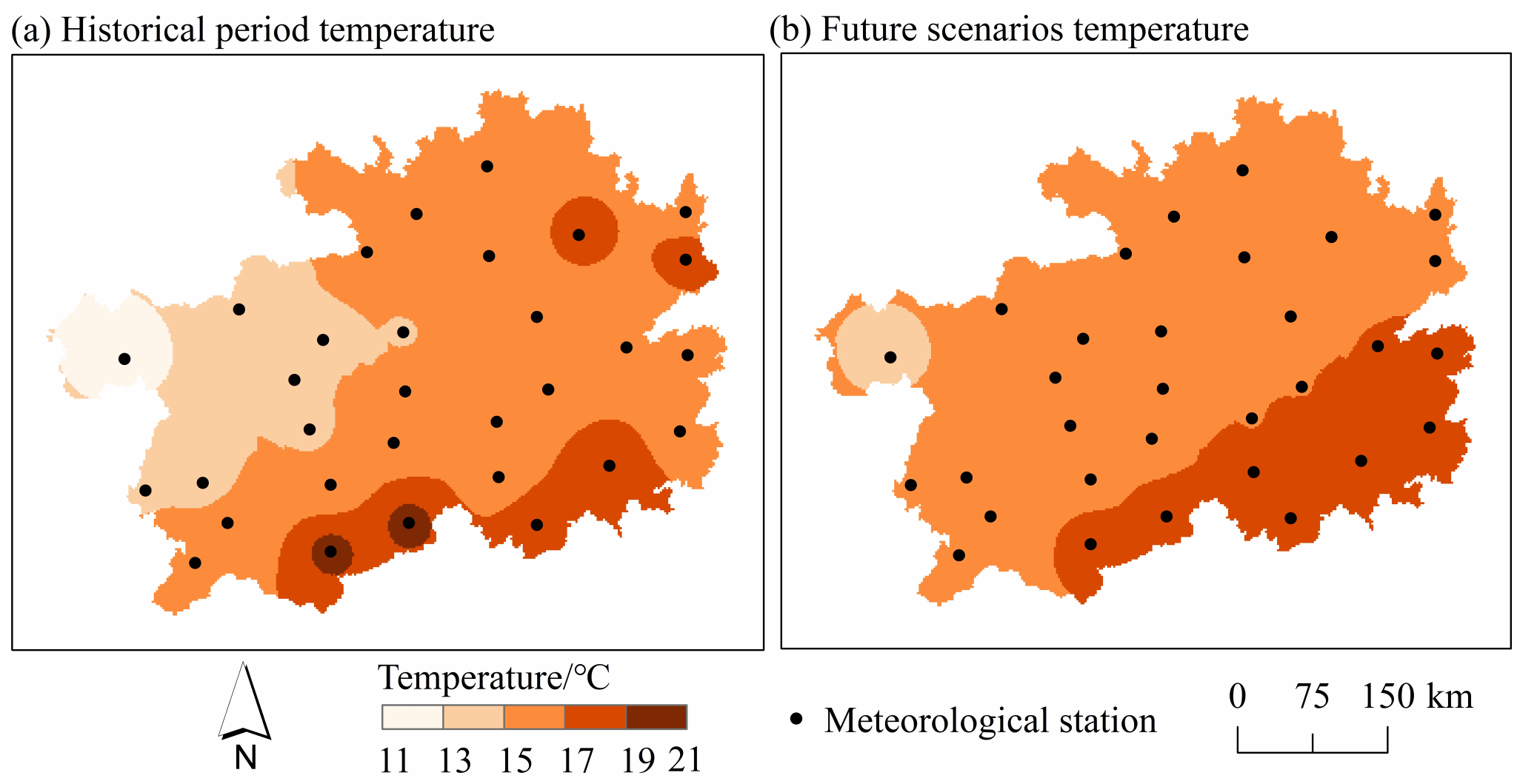
Fig. 10 Spatial distribution of temperature in historical and future periods.
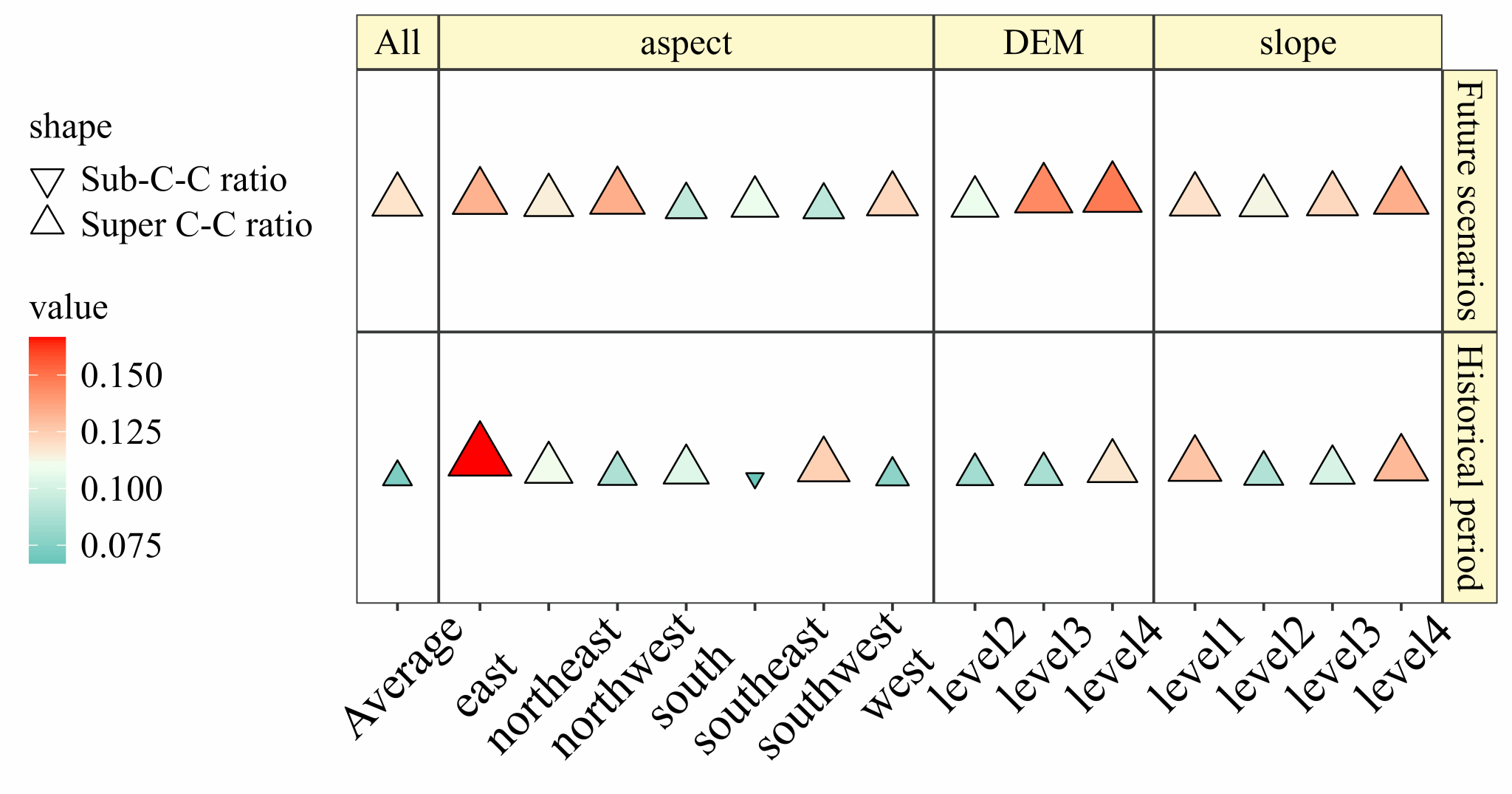
Fig. 11 Summary of the intensity of the response of extreme rainfall to changes in temperature.
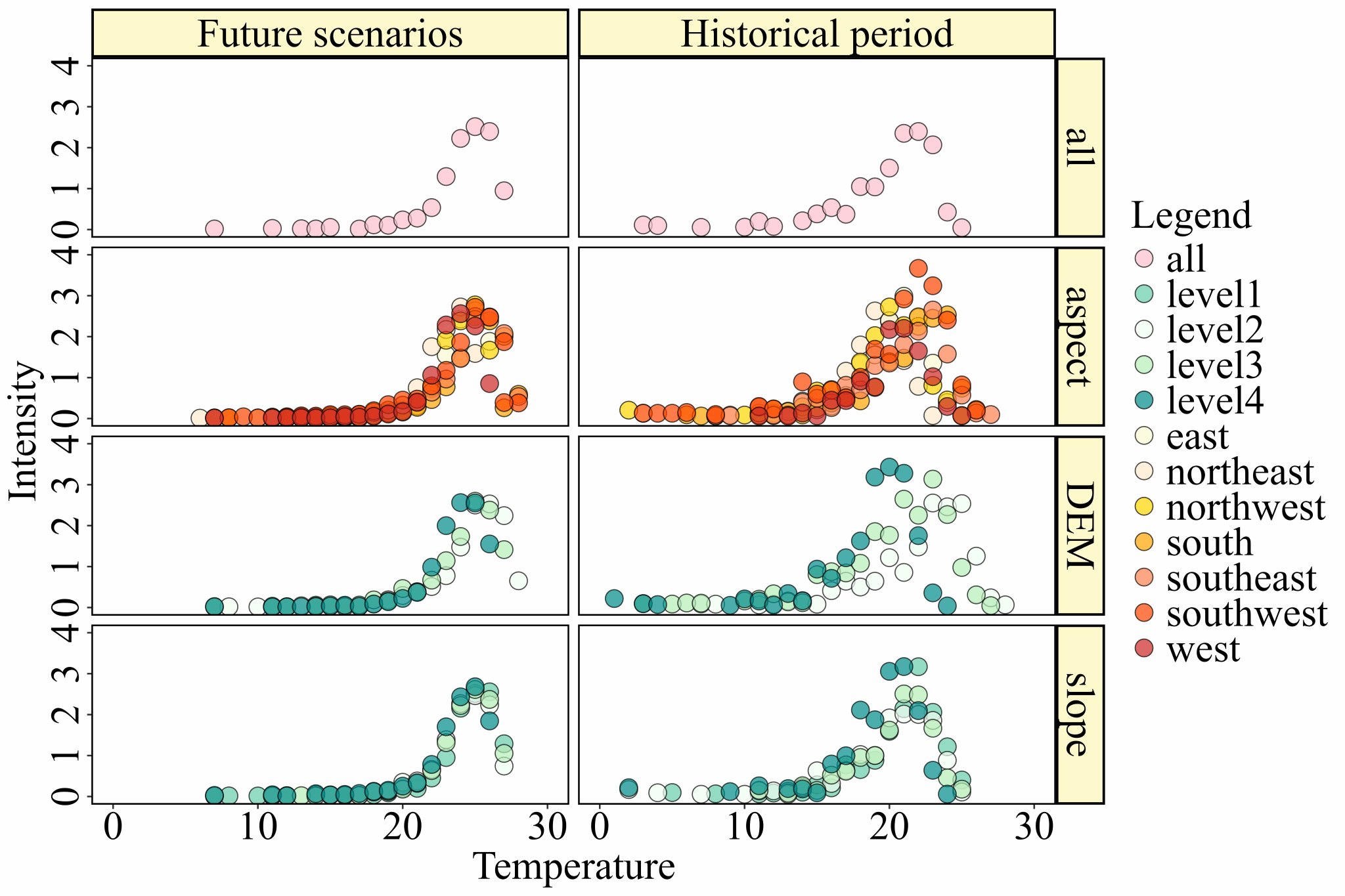
Fig. 12 Structure of the response of extreme rainfall to temperature change.
Table 1
Spatio-temporal resolution of CMIP6 data and its sources.

Table 2
Criteria for structural grading of underlayment
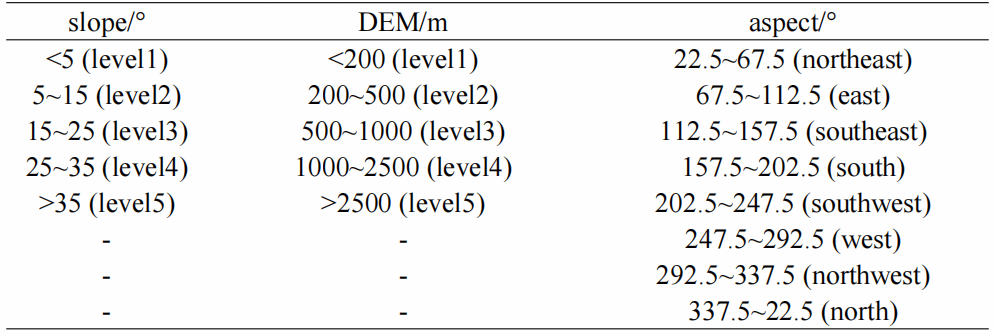
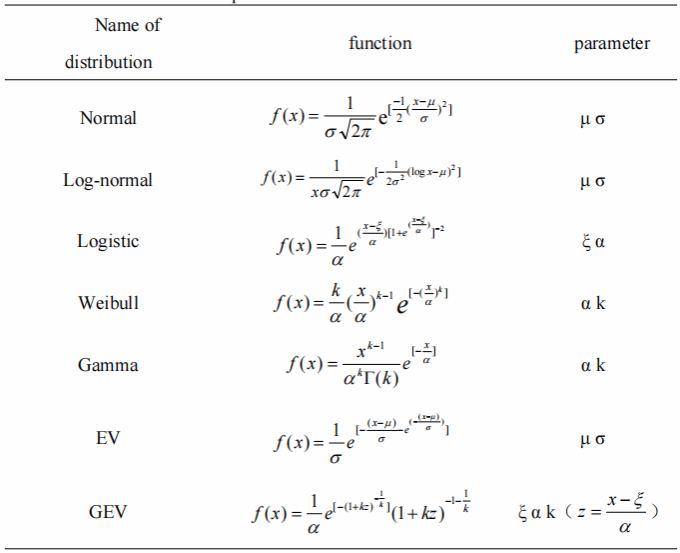
Table 3
Distribution function and its parameters
项目资助:该研究获得贵州省水利厅自然科学基金项目(KT202237)、国家自然科学基金项目(u1612441,41471032)等项目的联合资助。
期刊简介:《Scientific Reports》是Nature出版集团旗下的一本开放获取(Open Access)期刊,该期刊托管在NATURE.COM上,作为自然出版集团旗下80多种期刊的主页,吸引了全球数百万科学家的关注。它涵盖了自然科学的多个学科,包括自然科学、医学、工程学和心理学等。期刊目前位于中科院分区二区,当前影响因子为3.8。
第一作者简介:谭红梅(2000—),女,汉族,贵州湄潭人,共青团员。bat365登录平台入口2022级地图学与地理信息系统硕士研究生。参与导师多项科研课题,曾获研究生国家奖学金、三好学生、研究生二等学业奖学金等荣誉,主要从事喀斯特水文水资源与遥感研究。在研期间取得代表性研究成果如下:
[1] Tan, H., He, Z., Yu, H. et al. Characterization of extreme rainfall changes and response to temperature changes in Guizhou Province, China. Scientific Reports 14, 20495 (2024).
[2] 谭红梅,贺中华,陈莉会,等. 贵州省极端降雨特征及其影响因子[J]. 山地学报,2023,41(05):748-758.

导师简介:贺中华,男,贵州兴义人,教授、博士生导师。主要从事喀斯特流域干旱、喀斯特流域洪水及洪水资源化机理、喀斯特流域水资源、枯水及枯水资源承载力、喀斯特流域生态水遥感定量模型、喀斯特高原湖泊富营养化高光谱遥感监测等方面的研究。主持国家基金面上项目“中国南方喀斯特流域结构的水文干旱驱动机制(41471032)”1项、国家重大专项“筑坝流域‘三水’分配、转化过程与水量安全” 子课题——水文系统辨识与统计诊断,系统分析气候变化、土地利用演变等因素对水文过程的影响(u1612441)”1项,参与完成国家基金项目“岩溶地下河与地表河汇流混合过程中河流无机碳行为研究(41263011)”、“喀斯流域结构与枯水径流特征分析(40061001)” 2项,主持及参与省级 7项、厅级8项、博士基金1项,专箸《喀斯特流域洪、枯水资源化机理与遥感应用模型研究》(科学出版社)1部。先后在《International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation》、《Scientific Reports》(Nature子刊)、《Water & Climate Change》、《Theoretical and Applied Climatology》、《Natural Hazards》,以及《地理科学》、《水土保持学报》、《自然资源学报》等学术期刊发表科研成果论文100余篇,荣获贵州省科技进步三等奖1项、贵州省水利厅科学技术进步一等奖1项。同时,是国家自然科学基金委项目函评专家,以及《Water Resources Research》、《Hydrology and Earth System Sciences》、《Journal of Hydrology》、《Advances in Water Resources》等期刊审稿专家。

成果链接:“Tan, H., He, Z., Yu, H. et al. Characterization of extreme rainfall changes and response to temperature changes in Guizhou Province, China. Scientific Reports 14, 20495 (2024)”
文章原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-71662-2
一审(校):谭红梅;二审(校):范艺馨;三审(校):赵翠薇

